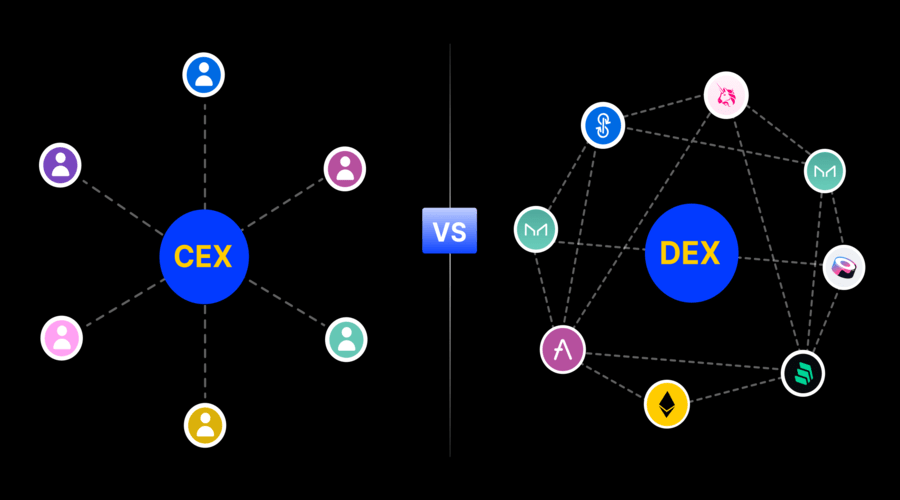
In the world of cryptocurrency trading, there are two main types of exchanges: decentralized exchanges (DEX) and centralized exchanges (CEX). Each type has its own set of characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. This article aims to provide a comparative analysis of decentralized exchanges versus centralized exchanges, exploring their differences, benefits, and potential drawbacks.
What is a Centralized Exchange?
A centralized exchange refers to a platform where buyers and sellers trade cryptocurrencies under the control and management of a centralized authority. These exchanges act as intermediaries and provide services such as order matching, trade execution, and asset storage. Examples of centralized exchanges include Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken. A centralized exchange refers to a platform where buyers and sellers trade cryptocurrencies under the control and management of a centralized authority. It acts as an intermediary, facilitating the matching of orders and executing trades. Users typically deposit their funds into the exchange’s wallets and trade within the platform. Centralized exchanges offer features such as order books, trading pairs, and advanced trading tools. They prioritize liquidity, user experience, and security measures to provide a reliable and efficient trading environment. Examples of centralized exchanges include Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken.
Advantages of Centralized Exchanges
Centralized exchanges offer several advantages:
- Liquidity: Centralized exchanges typically have higher trading volumes and liquidity compared to decentralized exchanges. This makes it easier for traders to execute large orders without significantly impacting the market price.
- User Experience: Centralized exchanges often have user-friendly interfaces, making it easier for beginners to navigate and trade cryptocurrencies. They offer features like charting tools, order books, and trading pairs, enhancing the overall user experience.
- Security Measures: Centralized exchanges invest heavily in security measures to protect user funds. They employ advanced security protocols, cold storage for assets, and two-factor authentication, minimizing the risk of hacking or theft.
Disadvantages of Centralized Exchanges
However, centralized exchanges also have some drawbacks:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Despite the security measures in place, centralized exchanges remain vulnerable to hacking and security breaches. If a centralized exchange is compromised, user funds may be at risk.
- Custodial Control: Centralized exchanges require users to deposit their funds into the exchange’s wallets, giving the platform custodial control over the assets. This means users must trust the exchange to safeguard their funds.
- Regulatory Dependence: Centralized exchanges are subject to regulatory compliance and may require users to provide personal information for Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) procedures. This compromises user privacy and can limit accessibility for individuals in regions with strict regulations.
What is a Decentralized Exchange?
A decentralized exchange operates on a peer-to-peer network, allowing users to trade cryptocurrencies directly with each other without the need for intermediaries. Smart contracts and blockchain technology facilitate the exchange process. Examples of decentralized exchanges include Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap. A decentralized exchange (DEX) is a platform that enables peer-to-peer cryptocurrency trading without the need for intermediaries or a centralized authority. It operates on a decentralized network, typically utilizing smart contracts and blockchain technology to facilitate secure and transparent transactions. In a DEX, users retain control of their funds and trade directly with each other. This decentralized nature eliminates the need for KYC procedures and provides greater privacy and autonomy for users. Examples of decentralized exchanges include Uniswap, SushiSwap, and PancakeSwap. DEXs are at the forefront of the decentralized finance (DeFi) movement, promoting financial inclusivity and innovation in the cryptocurrency space.
Advantages of Decentralized Exchanges
Decentralized exchanges offer several advantages:
- Security and Trust: Decentralized exchanges eliminate the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of hacking or theft. Users have full control over their funds as they trade directly from their wallets, enhancing security and trust.
- User Privacy: Decentralized exchanges prioritize user privacy as they do not require users to provide personal information or undergo KYC procedures. This makes them appealing to individuals seeking anonymity and privacy.
- Regulatory Independence: Unlike centralized exchanges, decentralized exchanges operate in a more regulatory-agnostic manner. They provide access to cryptocurrencies without the need for regulatory approvals or restrictions, expanding accessibility for users globally.
Disadvantages of Decentralized Exchanges
However, decentralized exchanges also have some drawbacks:
- Liquidity Challenges: Decentralized exchanges often face liquidity challenges, especially for less popular tokens. This can result in higher slippage and lower trading volumes, making it harder to execute large orders.
- Complexity: Decentralized exchanges can be more complex for beginners, requiring a basic understanding of blockchain technology, wallet management, and interacting with smart contracts. This may deter less tech-savvy users from participating.
- Transaction Speed: Decentralized exchanges rely on blockchain networks for transaction confirmations, which can result in slower transaction speeds compared to centralized exchanges. This may cause delays in executing trades.
Security and Trust
In terms of security and trust, decentralized exchanges offer a higher level of protection against hacking and theft due to their elimination of centralized points of failure. However, users must still exercise caution and ensure they use secure wallets and verify the legitimacy of the smart contracts involved.
Liquidity
Centralized exchanges generally have higher liquidity, providing better trading opportunities for large-volume traders. Decentralized exchanges, on the other hand, may struggle with liquidity for less popular tokens, impacting trading efficiency. Liquidity is a crucial aspect of financial markets, including cryptocurrency exchanges. In the context of exchanges, liquidity refers to the ability to buy or sell an asset quickly and at a fair price without significantly impacting its market price. A liquid exchange has a deep order book and high trading volumes, allowing traders to execute orders smoothly. Higher liquidity provides several benefits, such as reduced slippage, better price discovery, and increased trading opportunities. Centralized exchanges generally have higher liquidity due to their larger user base and market-making activities. However, decentralized exchanges are continuously working to improve liquidity through mechanisms like automated market makers and liquidity pools.
User Privacy
Decentralized exchanges prioritize user privacy by eliminating the need for personal information and KYC procedures. Centralized exchanges, however, often require users to provide personal data, compromising privacy.
Regulatory Compliance
Centralized exchanges must comply with regulatory requirements, including KYC and AML procedures. Decentralized exchanges, being more regulatory-agnostic, offer greater freedom of access for users, especially in regions with strict regulations. Regulatory compliance is an important aspect for both centralized and decentralized exchanges in the cryptocurrency industry. It refers to adhering to the legal and regulatory requirements set by governing authorities, such as Know Your Customer (KYC) and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) regulations. Centralized exchanges typically have more stringent compliance measures in place due to their centralized nature and the need to operate within existing financial regulations. They require users to provide personal information and undergo verification processes. Decentralized exchanges, while often offering more privacy, may face challenges in meeting regulatory requirements. Striking a balance between regulatory compliance and user privacy is a significant challenge for the cryptocurrency industry as it continues to evolve.
Accessibility
Decentralized exchanges provide access to cryptocurrencies without geographic restrictions, allowing users from any part of the world to participate. Centralized exchanges, on the other hand, may have restrictions based on geographical location and regulatory compliance.
User Experience
Centralized exchanges focus on providing user-friendly interfaces and comprehensive trading features, catering to both beginners and experienced traders. Decentralized exchanges may have a steeper learning curve and require more technical knowledge.
User experience (UX) plays a crucial role in the success of any exchange, including cryptocurrency exchanges. In the context of exchanges, user experience refers to the overall satisfaction and ease of use that traders and users experience while interacting with the platform. A positive user experience includes factors such as intuitive user interfaces, responsive design, efficient order placement and execution, clear navigation, comprehensive trading features, and reliable customer support. Centralized exchanges often focus on providing user-friendly interfaces and educational resources to cater to both beginners and experienced traders. Decentralized exchanges strive to improve user experience by enhancing user interfaces and simplifying the process of interacting with smart contracts and decentralized protocols.
Innovation and Future Potential
Decentralized exchanges have been at the forefront of innovation in the cryptocurrency space. They have pioneered concepts such as automated market makers and yield farming, driving the evolution of decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both decentralized exchanges and centralized exchanges have their own unique characteristics and advantages. Centralized exchanges offer higher liquidity, better user experience, and enhanced security measures. On the other hand, decentralized exchanges prioritize user privacy, regulatory independence, and foster innovation within the DeFi ecosystem. Choosing between the two depends on individual preferences, risk tolerance, and trading requirements.
FAQs
- Are decentralized exchanges safer than centralized exchanges? Decentralized exchanges eliminate centralized points of failure, reducing the risk of hacking or theft. However, users must still exercise caution and follow best security practices.
- Do centralized exchanges require KYC procedures? Yes, most centralized exchanges require users to undergo KYC procedures to comply with regulatory requirements.
- Can decentralized exchanges handle large trading volumes? Decentralized exchanges may face liquidity challenges, making it harder to execute large orders efficiently.
- Which type of exchange is more suitable for beginners? Centralized exchanges often offer user-friendly interfaces and educational resources, making them more beginner-friendly compared to decentralized exchanges.
- Are decentralized exchanges the future of cryptocurrency trading? Decentralized exchanges have pioneered innovative concepts within the DeFi ecosystem and hold significant potential. However, centralized exchanges will likely continue to coexist, catering to different user preferences and trading needs.